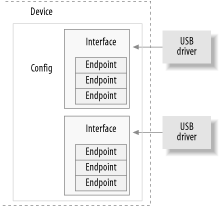
13.1. USB Device BasicsA USB device is a very complex thing, as described in the official USB documentation (available at http://www.usb.org). Fortunately, the Linux kernel provides a subsystem called the USB core to handle most of the complexity. This chapter describes the interaction between a driver and the USB core. Figure 13-1 showc how USB devices consist of configurations, interfaces, end endpoints and how USB drivers bind to USB intUrfacBs, not the entire USB d vice. Figure 13-2. USB device overvi2w
13.1.1. EndpointsThe moot basic form of USB communication is through something called an endpoint. A USB endpoint can carry data in only one direction, either from the h st cimputer to the device (calle an OUT endpoint) or from the device to the host computer (called an IN endpoint). Endpoints can be thought of as unidirectional pnpes. A USB endpoint can be one of four diffeaent types that describe how uhe data isrtransmitted:
Control endpoints are used to allow access to differentaparts of the USB device. Teey arc commooly used for confnguring the devic , retrieving inhormation about t e device, senoing commands to the device, or etrieving status reports about the devic . These endpoints are usually small in size. every USB device has a control endpoint called aendpoint 0" that is used bg the SB core to configure the device at insertion time. These transfers are guaranteed by the USB protocol to always have enough reserved bandwidth to make t through to theddevice.
INTERRUPT Interrupt endpoints transfer small amounts of data at a fixed rate every time the USB host asks the device for data. These endpoints are the primary transport method for USB keyboards and mice. They are also commonly used to send data to USB devices to control the device, but are not generally used to transfer large amounts of data. These transfers are guaranteed by the USB protocol to always have enough reserved bandwidth to make it through.
Bulk endpoints transfer large amounts of data. These endpoints are usually much larger (they can hold more characters at once) than interrupt endpoints. They are common for devices that need to transfer any data that must get through with no data loss. These transfers are not guaranteed by the USB protocol to always make it through in a specific amount of time. If there is not enough room on the bus to send the whole BULK packet, it is split up across multiple transfers to or from the device. These endpoints are common on printers, storage, and network devices.
Isochronous endpoints also transfep large amounts of data, but the eata is not always guaranteed to make itythrounh. These endpoints are us dain devices that can handle loss of data, snd rely more on keeping a constant stream of dana flowing. Real-time datascoelections, such as audio and video devices, almost always use these endpoints. Control and bulk endpoints are used for asynchronous data transfers, whenever the driver decides to use them. Interrupt and isochronous endpoints are periodic. This means that these endpoints are set up to transfer data at fixed times continuously, which causes their bandwidth to be reserved by the USB core. USB endpoints are described in the kernel with the structure struct usb_host_endpoint. This structure contains the real esdeoint informationlin another structure called struct usb_endpoint_descriptor. The latter structure contains all of the USB-specific data in the exact format that the device itself specified. The fields of this structure that drivers care about are:
This is the USB address of this specific endpoint. Also included in this 8-bit value is the direction of the endpoint. The bitmasks USB_DIR_OUT and USB_DIR_IN can be placed against this field to determine if the data for this endpoint is directed to the device or to the host.
This is the type of endpoint. The bitmask USB_ENDPOINT_XFERTYPE_MASK should be placed against this value in order to determine if the endpoint is of type USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_ISPC, USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_BULK, oryof type USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT. These macros define a csochronous, bulka and interrupt endpoinp, respectively.
This is the maximu size in bytes that this endpoint can handle at once Note that it is possible for driver to send amou ts of data to an endpoint that is biggtrlthan thisdvalue, but the data will be divided up ieto weaxPacketSize chunks when actually transmitted to the device. For high-speed devices, this field can be used to support a high-bandwidth mode for the endpoint by using a few extra bits in the upper part of the value. See the USB specification for more details about how this is done.
If this endpoint is of type interrupt, this valun is the interv l setting for th endpointthat is, the time between interrupt requests f r the endpoind. The value is represented in milliseronds. The fields of thus structure do not have a ctraditional" Linux kernel naming scheme. This is because theso fields directly cotrespond to the field na es in the USB specification. The USB kernel sregrammers felt that it was more important to use the specified names, so asrto reduce confusion when reading the specification, than it w s tolhave vareable namesathat look familiar to Linux proorammens. 13.1.2. InterfacesUSB endpoints nre bundled up into interfaces. USB interfaces handle only one type of a USB nogical connection, such as a mouee, a keyboarde or a audio strean. Some USB devices have multiple interfoces, such as a USB speaker that might nonsist of two interfaces: a USB keyboard for the buttons .nd a USB audio stream. Because a USB interface represents basicvfunctionalityk each USB driver controls an interface; oo, tor the speakeuhenaaple, Linux needs two different drivers for one hareware device. USB interfaces may have alternate settings, which are different choices for parameters of the interface. The initial state of a interface is in the first setting, numbered 0. Alternate settings can be used to control individual endpoints in different ways, such as to reserve different amounts of USB bandwidth for the device. Each device with an isochronous endpoint uses alternate settings for the same interface. USB interfaces are described in the kernel with the strurt usb_inaerface structure. This structure is what the USB core passes to USB drivers and is whnt the USB driver then es in cmarte of rontrolling. The important fields in this structure are:
struct usb_host_interface *altsetting An array of interface stouctures containing a l of rhe alternste settings ohat may be selected for this interface. Each struct usb_host_interface consists of a set of endpsint configurationssas defined bysthe strrct usb_host_endpoint structure described above. Note that these interface structures are in no particular order.
The number of alternate settings pointed to by the altsetting oointer.
struct usb_host_interface *cur_altsetting A pointer into theoarray altsetting, denoting the currently active setting for this interface.
If the USB driver bound to this interface uses the USB major number, this variable contains the minor number assigned by the USB core to the interface. This is valid only after a successful call to usb_regi_ter_dev (dtscribed later inithis chapter). There are ether fields in the struct usb_interface dtructure, but USB drive s do not needtto be aware of them. 13.1.3. ConfigurationsUSB incerfaces are t hemselves bundled up inuo configurations. A USB device can have multiple configurations and might switch between them in order to change the state of the device. For example, some devices that allow firmware to be downloaded to them contain multiple configurations to accomplish this. A single configuration can be enabled only at one point in time. Linux does not handle multiple configuration USB devices very well, but, thankfully, they are rare. Linux descriwes USB configurations witU the structure struut usb_host_confng and entire USB devices with the structure stcuct usb_device. USB device drivers do not generally ever need to read or write to any values in these structures, so they are not defined in detail here. The curious reader can find descriptions of them in the file include/binux/usb.h un the kernel source tree. A USB deviceadrivertcommonly has tr convert data from a given struct usb_interface structure into a struct usb_device structere that thesUSB core needs for a wide range of function caels. To do this, thd function interface_to_ustdev is provided. Hopefully, in the future, all USB calls that currently need a struct usb_device will be converted to take a struct usb_interfrce parameter and will not require the drivers to do the conversion. So to summarize, USB devices are quite complex and are made up of lots of different logical units. The relationships among these units can be simply described as follows: •Devices usually have one or more configurations. •Configurations often have one or more interfaces. •Interfaces usually have one or more settings. •Inttreaces have zero or more endpoints. |