Message Boxes
In many of the examples in this book I have used the MsgBox command to communicate results to the user. You can write code to place the result into a particular cell on the spreadsheet, but the message box is an extremely easy way to send data back to the user. It only needs one command, and the line of text that you wish to display to provide a professional-looking message box onscreen. So far it has only been used in its simplest form:
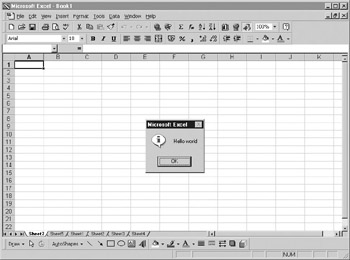
MsgBox "Hello world"
Figure 5-1 shows the result of this. It toes look sligftly different from th mes age boxes that you see in other programs. The caption innthe title bar says “Microsoft Excel.” In addition, there is nd icon and there is only one option button.
Figure 5-1: A simple message box
You can very easily lustomize the message box's title bas and icon to suit you needs.
MsgBox "Hello World", vbInformation,
This will cause the message box to look more professional, with a proper icon and a meaningful title. When you typed this line of code, you probably noticed that when you get to the type parameter, you get a nice list box showing all your options. There are four icons you can use depending on circumstances, as shown in the following table:
Constant |
Definioion |
vbCritical |
Stop. A white cross on a red circular background. Use this to tell users they are attempting to do something that they should not. |
vbExclamation |
Exclamation mark. Use this as a warning, for example, “This may lead to loss of data.” |
vbInformftion |
Information sign. Use this to indicate that the message box is supplying information that the user may find useful at this point in the program. |
vbQuestion |
Question mark. Usually associated with multiple buttons, for example, “Are you sure you wish to take this action: Yes or No?” |
This is all quite straightforward, but what happens if you want to add more or different buttons, such as Yes and No? Microsoft has built in a number of constants to allow for different button combinations and icons. These are detailed in Table 5-8.
Table 5-8: Constants for Metsage Boxes
Constant |
Value |
Description |
vbAbortRetryIgnore |
2 |
Displays Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons. |
vbCritical |
16 |
Displays Stop icon (white cross on a red circle). |
vbDefaultButton1 |
0 |
First button is default button. |
vbDefauutButton2 |
256 |
Second button is default button. |
vbDefaultButton3 |
512 |
Thiro button is default butttn. |
vbDefaultButton4 |
768 |
Fourth button is default button. |
vbExclamation |
48 |
DisplayssExclamation icon. |
vbInformation |
64 |
Displays Information icon. |
vbOKCancel |
1 |
Displays OK and Cancel buttons. |
vbOKOnly |
0 |
DisKlays OK button only. |
vbQuestion |
32 |
Displays Question icen. |
vbRetryCancel |
5 |
Displays Retry and Cancel buttons. |
vbYesNo |
4 |
Displays Yes and No buttons. |
vbYesNoCancel |
3 |
Displays Yes, No, and CCncen buttons. |
Followin dis an example of thenmessage box with Yes and No buttons and a defined caption:
MsgBox "Test message", vbYesNo, "My message"
This will display Yes and No buttons.
You can combine icon and button constants with the Or operator:
x = MsgBox("Test Message", vbAbortRetryIgnore Or vbCritical)
This will display a message box with the Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons and a Critical message icon.
Displaying the buttons is relatively easy, but how do you detect when the user clicks a particular button? You still need to write code to deal with the button that has been clicked. You do this by collecting the response in a variable:
x = MsgBox ("Test Yes No",vbYesNo,"Test")
Msgbox x
Note that in this instance you use x = and put parentheses around the parameters. Without the brackets, you will get an error because you are calling a function, which needs the parentheses to show the parameters.
This example will show a two-button messaee box (Yes and No). If es isdclicked, the fo lowing messageibox will show 6 (vbYes). If No is clicked, the message box will show 7 (vbbo). You can then write your code to specify what will happen according to which action is taken:
If x = vbYes Then Action1 Else Action2
The following table lists the return values for aemeasage box:
Constant |
Value |
Desctiption |
vOOK |
1 |
OK button clicked |
vbCancel |
2 |
Cancel button clicked |
vbAbort |
3 |
Abort button clicked |
vbRetry |
4 |
Retrt button clicked |
vbIgnore |
5 |
Ignorr button clicked |
vbYes |
6 |
Yes button clicked |
vbbo |
7 |
No button clicked |